Graphene oxide (GO) is a type of graphene that contains oxygen functional groups and has some interesting properties different than those of graphene. By reducing graphene oxide, reduced graphene oxide is obtained which is abbreviated to rGO. In this process, the functional groups of graphene are removed but it still contains residual oxygen, hetereatoms and structural defects which decrease its quality. Having less-quality compared to pristine graphene, rGO is still an outstanding material for various applications since it resembles an attractive cost and manufacturing processes compared to the pristine graphene. Especially, it is preferred in applications that call for a large amount of material.

Depending on the method of preparation of reduced graphene oxide, properties and morphology of the rGO can vary. Some preparation methods of reduced graphene oxide include:
- treating graphene oxide with hydrazine hydrate at 100°C for 24 hours
- exposure to hydrogen plasma for several seconds
- exposure to powerful pulsed light from xenon flashtubes
- heating the graphene oxide with urea as an expansion-reduction agent
- direct heating of graphene oxide in a furnace to very high temperatures
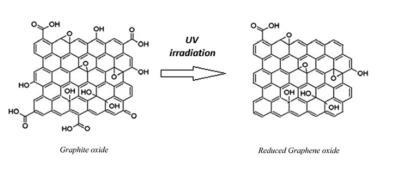
Applications of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO)
Electronics: rGO shows a great potential in electronics applications. It is used as a field effect transistor that has been used in chemical sensors and biosensors. In biosensors, detect hormonal catecholamine molecules, avidin and DNA. rGO is also used in light emitting diodes (LEDs) and solar cell devices. For these applications, having transparent electrode is important and rGO is a convenient for these devices.
Energy Storage: Nanocomposites of rGO is used for lithium-ion batteries, extensively. In these batteries, nanoparticles of insulating metal oxide are absorbed onto rGO which enhances the performance of these materials in lithium-ion batteries.
It is also used in many composite materials and printable graphene electronics.
Overall, rGO is a suitable material for many applications although it looks like less impressive when it is compared to graphene.
Read more about Reduced Graphene Oxide on nanografi.com:

Comments
Post a Comment