Fullerene is an allotrope of carbon, its structure consists of carbon atoms connected to each other by sigma or pi bonds in order to form a closed or partially closed mash with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The fullerene molecule can comprise many shapes and sizes such as tube, ellipsoid, sphere and etc. Since their discovery in 1980s, fullerene has drawn considerable attention for the subject of intense research, especially in electronics, materials science, and nanotechnology.
Even though fullerenes have remarkable electronic and chemical properties, they have poor solubility in polar solvents such as water. This poor solubility prevents fullerenes’ potential uses in biological applications. Thus, scientific studies have been carried out to improve the solubility of fullerene in polar solvents. The one heavily studied functionalized fullerene is the Polyhydroxylated Fullerene (PHF, also named as Fullerenol or Fullerol) leading to enhanced solubility.
The studies have shown that Polyhydroxylated Fullerene has such a structure that is composed of 60 carbon atoms and hydroxyl groups attached to carbons (-OH). PHF has over 40 hydroxyl groups that gives the material higher water solubility (over 50 mg/mL).
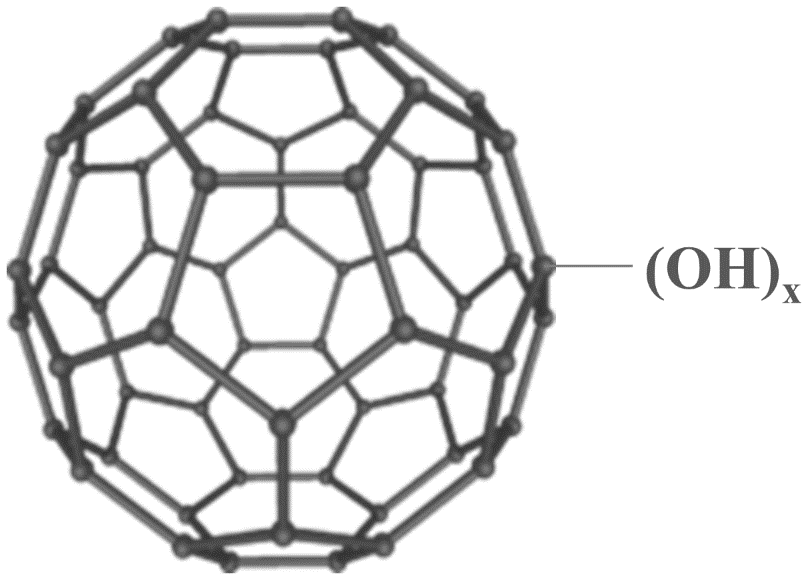
Figure 1: Chemical structure of a polyhydroxylated fullerene (x=12 to 42)
Synthesis of Polyhydroxylated Fullerene
During the synthesis of PHF, firstly nitrogen dioxide radicals which were generated by reaction of sodium nitrite with concentrated HNO3 are added to C60 molecule (Fullerene) and since PHF has high reactivity towards the addition reaction of nitrogen dioxide. The chemical reaction results in polynitro fullerene C60(NO2)n. Then, the hydrolysis of polynitro fullerenes in aqeous NaOH yields to corresponding polyhydroxylated fullerenes (Fullerenols) in moderate overall yields.
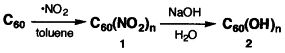
Properties of Fullerenols
- Enhanced solubility in polar solvents especially in water
- High antioxidant activity due to presence of free radical scavengers
- Exhibits antimicrobial activity as well
Application Areas
- Electronics Parts: Superconducting semiconductor, diodes, and transistors
- Optical Materials: Electronic camera, fluorescence display tube
- Energy: Solar battery, fuel cell, secondary battery
- Biological: Cosmetics, super drugs, anti-cancer drugs, chemotherapy drugs, anti-HIV drugs
- Industry: Polymer additives, high-performance coatings, memory materials, water-resistant materials
Read more about this material:



Comments
Post a Comment