Silver nanoparticles have been recently drawn into attention for extensive research interest since they have unusual optical, chemical, electronic and biological properties. The use of silver nanoparticles increased in various fields, including medical, food, industrial and consumer purposes because of their unique physical and chemical properties.

Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), demonstrate changeable and original properties depending on their size, structure, composition, crystallinity and due to their surface-to-volume ratio, they can considerably change physical, chemical, and biological properties. Therefore, they have been utilized for various applications. In order to use these nanoparticles in desired areas, synthesis of AgNPs are required. AgNPs can be synthesized in three ways by physical, chemical or biological methods. For the most part, pyhsical methods can not achieve enough yield and purity. Similarly, chemical methods can not provide enough purity however they can obtain high yield. Interestingly, biological methods seem to be the most efficient way of synthesizing AgNPs as these green approaches can produce high yield, high purity particles with a well-defined size and uniform distribution. Also, an environment-friendly way of synthesis of AgNPs displays much promise.
Silver Nanoparticle Dispersions
Dispersion, is basically a compostion of at least 2 materials which has at least 2 separate phases, one of which is continuous phase (matrix) and the dispersed phase usually in nano size. (Between the range 10 to 100 nm). In our case, silver nanoparticles are the dispersed phase that has only one phase boundary with the matrix phase.
AgNPs are used in a numerous technologies and combined into a wide range of consumer products which make use of their desirable antibacterial, optical, and conductive properties.
Biological Applications of AgNPs
AgNPs are being used in numerous biological and biomedical applications such as anti-viral, anti-cancer, anti-fungal, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory and so.
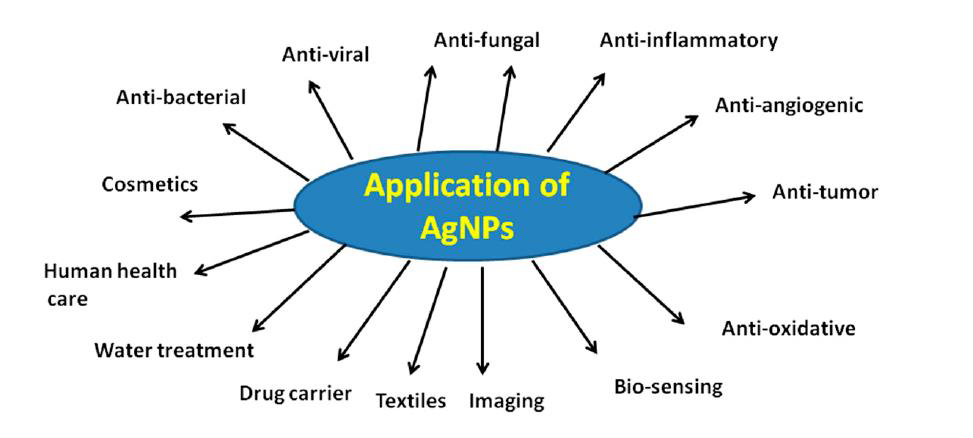
(image source: Silver Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, Properties, Applications, and Therapeutic Approaches, X.F. Zhang, W. Shen, International Journal of Molecular Science, 5 July 2016.)
AgNPs are vital for these application areas and potential anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-fungal agents due to their large surface-to-volume ratio and their specific crystallographic surface structure.
Electronic Applications
AgNPsare used in composites and electronically conductive adhesives (ECAs) in order to enhance the electrical and thermal properties of the materials. To be more specific, dispersion of silver nanoparticles in ECAs limits their conductivity if they are used as conductive fillers. To prevent this situation, AgNPs are reduced with ethanol and the presence of poly(N- vinylpyrrolidone) (PVP). In this process, PVP prevents the nanoparticles from aggregation to form larger particles. Moreover, thanks to presence of PVP, nucleation rate increases and this leads to a decrease in the average size of the particles which is a mainly desired parameter in the application.
To conclude, the unique properties of AgNPs make them vital and ideal for biomedical, electronical, optical applications. Also, they play an important role in nanotoxicology studies. Although silver nanoparticles play an important role in clinical studies, several parameters such as production method, the source of raw materials, accumulation, and toxicological cases to humans should be considered.
Comments
Post a Comment