Titanium dioxide is also called titania which occurs oxide of titanium in nature, and its resources are ilmenite, rutile, and anatase. It is a large-band gap semi-conductor. In 2014, world production exceeded nine million metric tons, and it has been valued at $13.2 billion. Since it has unique optical and chemical properties, titanium dioxide nanoparticles have been studied and numerous applications are found. They are also called ultrafine titanium dioxide. Small size add a significant property to nanoparticles of titanium oxide which makes it photocatalytic material. High chemical stability, and strong oxidizing power are also properties of titanium dioxide nanoparticles among others.
Figure: In the rutile titanium dioxide crystalline structure, titanium and oxygen atoms are shown as grey and red spheres respectively.
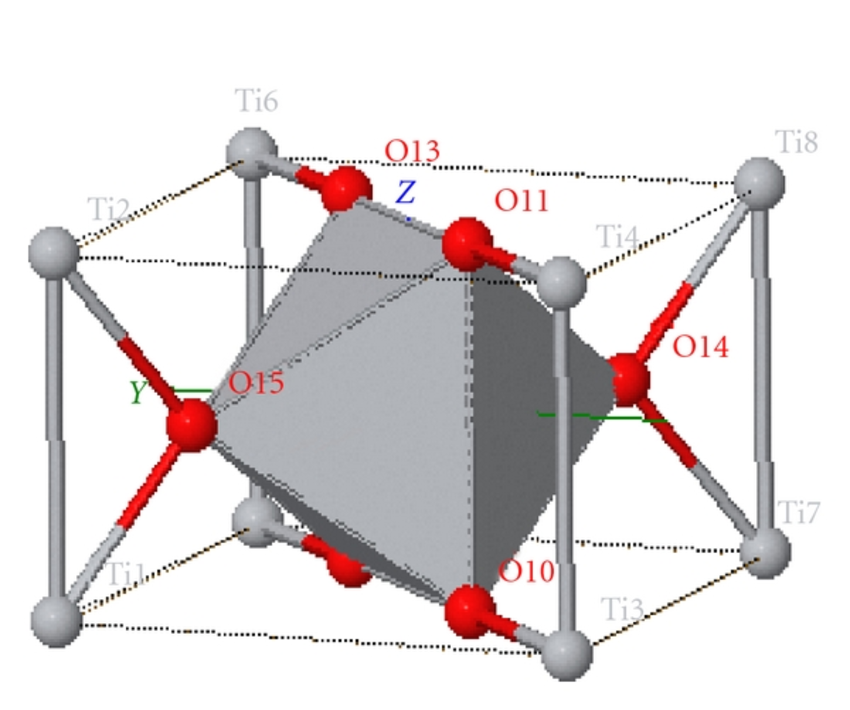
G. Narejo, and W. F. Perger, First Principles Computations of Second-Order Elastic Constants (SOEC) and Equations of state of Rutile TiO2, 2011.
In consideration of being a rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles as you can see the structure in the figure above, the nanoparticle one is more absorbent than larger size, and it has many synthesizing methods like Laser Ablation method. Since the band gap of rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles is 3 eV which is lower than band gap of zinc oxide, and it has already applications in semiconductor technology as sensors. Therefore, rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles are commonly studied in photonics, and semiconductor technology. It can be functionalized to absorb UV radiation in commercial applications. It can be additive or component of composites to insert photocatalytic activity to composites. One can also mix rutile and anatese to make band gap alignment.
A research group at Changwon National University conducted a study that they synthesized rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles using sol-gel method followed by hydrolysis of TiCl4 at low temperature. They also found that the size is 26.4 nm at 300 C°, and the size increase with temperature. Another research group studied photocatalytic applications of room temperature rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles, and they concluded that it shows a remarkable photocatalytic efficiency on degradation of MB Dye, RB Dye, and PNP. They examined the degradation of materials via UV-Vis spectrophotometry. As a result, degradations of MB Dye, RB Dye, and PNP are 97%, 98%, and 80% respectively.
Rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles offer tremendous applications in many fields. There are researchers conducting experiments to develop new and cost effective synthesis methods, and many more applications will be found.
Comments
Post a Comment