Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula ZnO. The applications of zinc oxide compound dates back even to antiquity. ZnO originated many centuries ago as an impure by product of copper smelting process. However, modern rediscovery of ZnO and its potential applications began in 1950s.
ZnO micron powder is a white powder which is not soluble in water, and it is largely used as an additive in numerous materials and products. ZnO occurs naturally as a mineral called zincite, however, most of the zinc oxide is produced synthetically. Zinc oxide and zinc oxide micron powders have gained considerable interest in the last decades due to their combination of unique properties. Zinc oxide compound exhibits polytypes, in other words, it has more than one possible crystal structure. It can exist in both in the hexagonal wurtzite and cubic zinc blende structure.
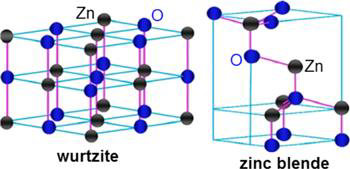
Figure 1: A schematic representation of ZnO crystal structures ; wurtzite and zinc blende
ZnO micron powders have various and beneficial properties. Thus, ZnO has drawn a lot of attraction in both scientific and industrial application areas.
Properties of ZnO Powder
Chemical Properties
- ZnO is an amphoteric oxide. It is nearly insoluble in water, however, it can dissolve in most acids, such as HCl.
- It has high melting and boiling points, 1975⁰C and 2360⁰C respectively.
Biological Properties
- ZnO has antibacterial and deodorizing properties, so it is used in medical applications.
Mechanical Properties
- It has high heat capacity and heat conductivity, low thermal expansion and also high melting temperature. These properties make ZnO beneficial for ceramics.
- It has unusually long lifetime.
Electronical Properties
- It is a wide-bandgap n-type semiconductor of the II-VI semiconductor group.
- It has good transparency, high electron mobility, and strong room-temperature luminescence.
- ZnO has a relatively large direct band gap of ~3.3 eV at room temperature. Having a large direct band gap brings some advantages such as higher breakdown voltages, ability to sustain large electric fields, lower electronic noise, and high-temperature and high-power operation.
- In addition, ZnO have high breakdown strength and high saturation velocity.
Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Micron Powders
There are various methods that had been formulated and applied to produce zinc oxide powders. The techniques which are used in synthesizing ZnO powders, include hydrothermal, spray pyrolysis, and laser ablation. However, these techniques require high temperatures and also due to high temperature, processes result in high production cost.
ZnO powders are generally synthesized by sol-gel processing. Sol-gel process is more frequently used because it can synthesize ZnO powder at low temperatures.
ZnO powders are generally synthesized by sol-gel processing. Sol-gel process is more frequently used because it can synthesize ZnO powder at low temperatures.
Application Areas of Zinc Oxide Powders
- Rubber Manufacturing
- UV absorber
- Food Additive
- Cigarette Films
- Coatings for Metals
- Corrosion prevention in Nuclear Reactors
- Ceramic Industry
- Medicine
Comments
Post a Comment