Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. For example leaf insect is a very good example for a camouflage from the nature or people make camouflage for military purposes to hide from their enemies.

Camouflage of leaf insect
Thermal camouflage is the appearance of being the same temperature as one's environment and this is a very different concept and much more difficult from the camouflage that we used to know. Thermal camouflage, has been an outstanding challenge which requires an ability to control the emitted thermal radiation from the surface. Let us see what is meant by saying thermal camouflage!
Scientist have created a graphene-based material that can outwit thermal cameras by masking hot objects. By the help of a film which provides a layer of camouflage by appearing to match the ambient temperature, potentially making the object it's covering seem invisible to the cameras.
How did the scientists achieve this? They combined graphene, nylon, gold and polythene coated with a liquid containing charged molecules. Applying three volts to the film pushes the charged ions into the graphene, which reduces the infrared light that the material emits and increases how reflective it is. The film takes just a few seconds to adapt to the appearance of the ambient temperature, and it works at between 25 and 38 degrees Celsius.
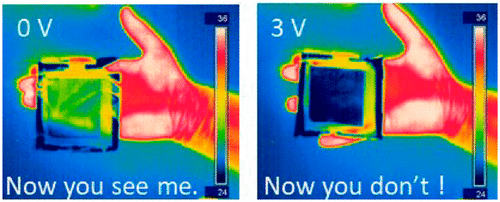
There are many uses of this material. The military, for instance, might be interested in how well it works during nighttime operations -- a normal human body's temperature is 37.3 degrees Celsius, just inside the effective range. The researchers behind the material say it could be useful in adaptive heat shields for satellites, too.
Maybe the most important chemical in this study is Graphene. Graphene is an atomic-scale hexagonal lattice made of carbon atoms
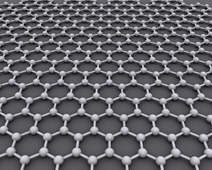
Structure of Graphene
Graphene is a semi-metal with small overlap between the valence and the conduction bands (zero bandgap material). It is an allotrope (form) of carbon consisting of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice.It is the basic structural element of many other allotropes of carbon, such as graphite, diamond, charcoal, carbon nanotubes and fullerenes.
Graphene has many uncommon properties. It is the strongest material ever tested, conducts heat and electricity efficiently, and is nearly transparent. Graphene shows a large and nonlinear diamagnetism, greater than that of graphite, and can be levitated by neodymium magnets.
You may order different types of Graphene products via our website:
Comments
Post a Comment