Cellulosic nanoparticles generally known as nanocellulose, have got interest from the scientific community because of their biodegradability, strength, and other characteristics. Sustainability and green issues continue as top priorities for many businesses and individuals, stimulating the search for nonpetroleum-based structural materials like bionanocomposites that are biodegradable, high performing, and lightweight.
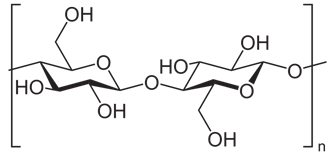
Cellulose Structure
So it can be said that because of its high biocompatibility, bio-degradability, low-cost and easy availability, cellulose finds application in disparate areas of research. Cellulose is the most abundant and renewable biopolymer in nature. It is the main constituent of plant cell walls in wood, cotton, hemp and other plant-based materials and plays an essential role in maintaining plant structural phase. Cellulose is also synthesized by marine animals such as tunicates, algae, fungi and several bacteria species. Cellulose is a carbohydrate homopolymer consisting of β-d-glucopyranose units joint together by β-1,4-glycosidic linkage. Cellulose fibrils are highly insoluble and inelastic but able to provide mechanical support to the tissues where they resides.
Crystalline cellulose has interesting mechanical properties for use in material applications. Its tensile strength is about 500MPa, similar to that of aluminium. Its stiffness is about 140–220 GPa. Films made from nanocellulose have high strength (over 200 MPa), high stiffness (around 20 GPa) and high strain(12%). Its strength/weight ratio is 8 times that of stainless steel. Fibers made from nanocellulose have high strength up to 1.57 GPa and stiffness up to 86 GPa.
Because of the positive properties given above, nanocellulose has found application in different research fields such as the biomedical, energy, environmental and water related fields.
Nanocellulose can be used in the area of paper and paperboard manufacture. Nanocelluloses are expected to enhance the fiber-fiber bond strength and, hence, have a strong reinforcement effect on paper materials.
As described above the properties of the nanocellulose makes an interesting material for reinforcing plastics. Nanocellulose improves the mechanical properties of, for example, thermosetting resins, starch-based matrixes, soy protein, rubber latex, poly(lactide). The composite applications may be for use as coatings and films, paints, foams, packaging.
Nanocellulose can be used as a low calorie replacement for today’s carbohydrate additives used as thickeners, flavour carriers and suspension stabilizers in a wide variety of food products and is useful for producing fillings, crushes, chips, wafers, soups, gravies, puddings etc. The food applications were early recognised as a highly interesting application field for nanocellulose due to the rheological behaviour of the nanocellulose gel.
Nanocellulose can be used as super water absorbent material.
Freeze-dried nanocellulose aerogels used in sanitary napkins, tampons, diapers or as wound dressing.
The use of nanocellulose as a composite coating agent in cosmetics e.g. for hair, eyelashes, eyebrows or nails.
You can get nanocellulose depending on your research needs from the link given below:
Comments
Post a Comment