Image retrieved from: http://phys.org/news/2013-10-major-graphene-solar...
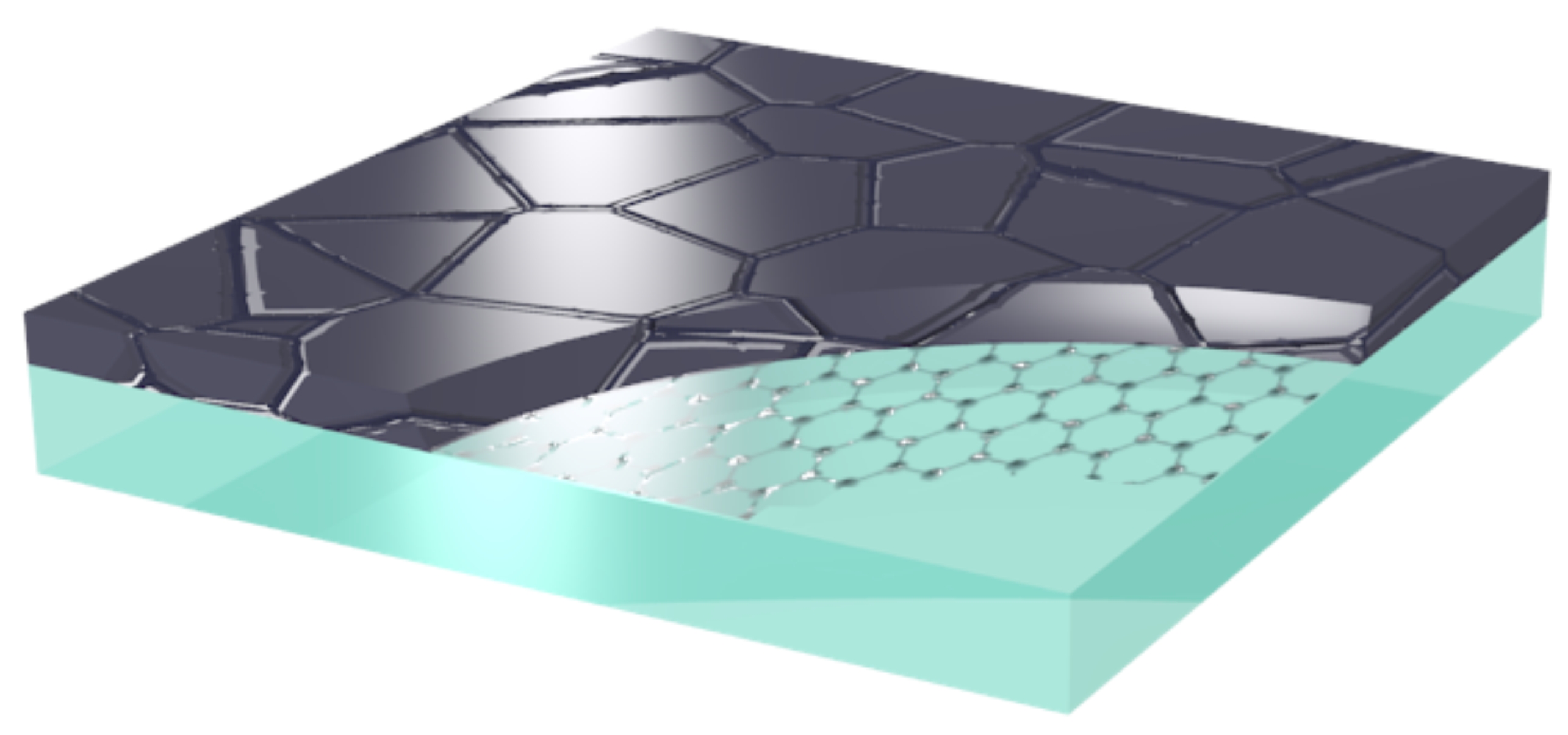
Studies in the Center of Multidimensional Carbon Materials (CMCM), within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) have shown protection of glass from corrosion by graphene coating.
Glass is a most common packaging material for protection of medicine and chemicals due to its high degree of resistivity towards corrosion and chemicals. However, some glass types can corrode over time at high humidity and pH conditions which will cause to decrease in its transparency and strength. Therefore, silicate glass corrosion under high humidity is a most serious problem especially for pharmaceutical, environmental and optical industries in hot and humid climates.
With the adsorption of water on the glass surface, hydrogen ions of water diffuse into glass and exchange with the sodium ions present in the glass surface. Then, pH of the water near the glass surface increases leading to dissolving of silicate structure of glass. To protect the glass surface, thin, transparent and good barrier material to chemical attack are needed for an ideal protective coating. Single layer Graphene with its chemical inertness, thinness and high transparency makes Graphene very promising for the coating of glass surface. In addition, Graphene can act as barrier for the chemical attacks. Therefore, Graphene can be used as protective layer for corrosion, oxidation, friction, bacterial infection, electromagnetic radiation etc.
According to the research at IBS, one or two atom thick layer can protect the glass from corrosion and scientist says that if the production of large amounts of higher quality graphene sheets on the glass surface is reached, then graphene coating on glass will be applicable in industrial scale.
For more information: http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/acsnano.6b043...
To find related protucts, visit our website: http://nanografi.com/graphene/
Posted by Müberra GÖKTAŞ on October 31, 2016
Comments
Post a Comment