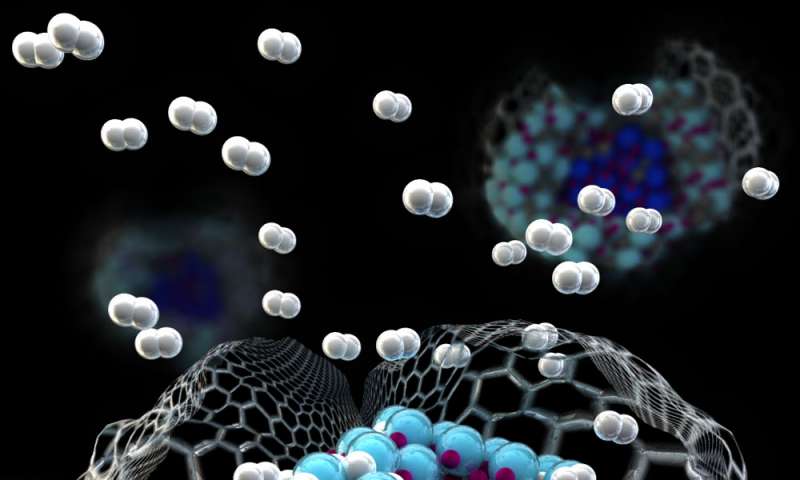
Nanomaterials with such properties show high potential for high quantity storage and fast adsorption and release of the hydrogen. Nanomaterials such as, nanoparticles, nanotubes, nanocomposite, and nanofibers are used and studied for these applications. Continuous research for the synthesis and the characterization of new nanomaterials is conducted for the improvement of the existing materials and the introduction of new ones that may have extraordinary properties.
The most important property of these nanomaterials is the high surface area and volume to mass ratio. This enables them to interact with more hydrogen atoms and to have ability to store mare of them. Moreover, it allows them to have more space in the bottom which speed up the adsorption and the release process. Some examples of these materials are lithium nitride, platinum nanoparticles, borohydrides nanoparticles, carbonaceous nanomaterials such as graphene and nanotubes.
Posted by Mohammed ZABARA on March 09, 2017
Comments
Post a Comment