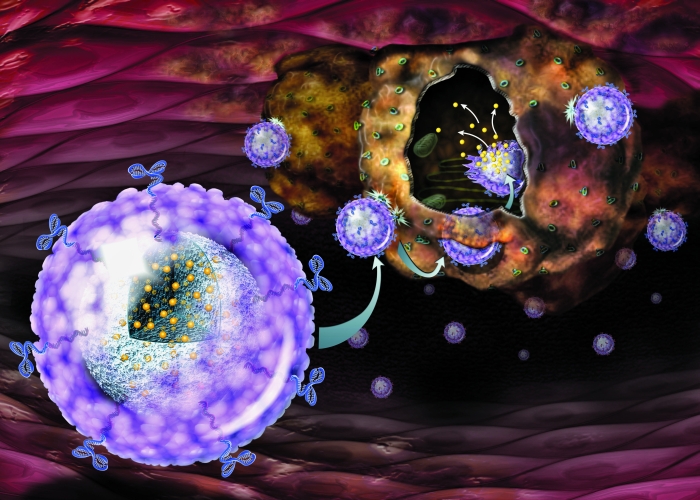
Drug delivery is one of the most important subject of research in medical sciences. The increase of the drug efficacy and the reduction of the side effects are among the goals of the research in this field. Scientists are working on the development of metallic nanoparticles which target the infected cells without doing harm to other neighbor cells. Au (Gold) nanoparticles, Ag (Silver) nanoparticles, Fe (Iron) nanoparticles and Cu (Copper) nanoparticles are the most researched nanoparticles which show high potential in site-specific drug delivery. These nanoparticles have unique physical and chemical properties such as, plasmatic resonance, fluorescent enhancement, and catalytic activity enhancement which make them very fascinating materials in drug delivery applications.
Retrieved from: http://nanoparticles.org
If we take a look at some examples of the metallic nanoparticles in drug delivery applications, we can realize the future potential of these particles. For example, Au, 99.99+%, 50-100 nm nanoparticles can be chemically functionalized with roughly 120,000 distinct molecules, which is two times higher than the surface loading capabilities of liposomes. Another example can be illustrated by Fe (Iron) nanoparticle 99.55+%, 90-100 nm, and Fe3O4 (Iron Oxide) nanoparticles, 18-28nm, Purity 98.45+%, which are MRI-monitored magnetic targeted nanoparticles. These nanoparticles can be directed toward the targeted cells using their magnetic properties. Variety of examples are available for different nanoparticles and an extensive research is being done to enhance the properties of these particles and to discover more applications for them in medical field.
Posted by Mohammed ZABARA on October 18, 2016
Comments
Post a Comment