Bottom-up approach depends on the synthesis of the metallic nanoparticles starting from the atoms of the metals. The main principle is to transfer the metallic substance into atoms in a process called nucleation and then to control the growth of the atoms until they reach the desired nano-size. Nucleation can be reached by the extensive heat of the metals in the gas phase or by the reduction of the metallic complexes in liquid phase conditions where the growth can be controlled by surfactant or stabilizer. The main methods for the preparation of the metallic nanoparticles in the gas phase are Pyrolysis, Gas condensation (Chemical Vapor Deposition), and Laser ablation. Here we discuss the preparation of the metallic nanoparticles by Pyrolysis and we leave the discussion of the other method for the next blogs.
In Pyrolysis the precursor is prepared in a precursor solution and heated in specific process to evaporate the solvent and form the nanoparticles. The most used method is spray pyrolysis in which the solution undergoes aerosol process that atomizes the precursor solution and heats the droplets to produce solid particles.
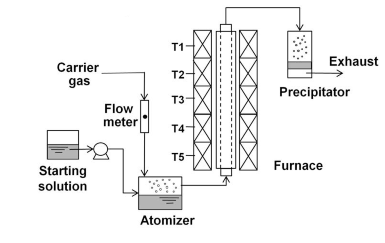
Image retrieved from: Advanced Powder Technology 20 (2009) 283–292, doi:10.1016/j.apt.2009.07.001
Different metallic, metallic oxide nanoparticles and nanocomposite particles can be prepared by this method. The shape and the size of the prepared nanoparticles can be adjusted by adjusting the composite of the precursor solution and the heat of the furnace. Some of the shapes that can be obtained are dense nanoparticles, shell-structured nanoparticles, hallow nanoparticles, and foam nanoparticles. Examples of nanoparticles and composite that are produced by pyrolysis are, Co (Cobalt Nanoparticles), Cu (Cupper Nanoparticles), Fe (Iron nanoparticles), Ti (Titanium Nanoparticles), TiO (Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles), Bi2O3 (Bismuth Oxide Nanoparticles), ZnO (Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles), ZnO/SiO2 (Zinc Oxide / Silicon Oxide Nanocomposite).
Posted by Mohammed ZABARA on November 30, 2016
Comments
Post a Comment