Nanocellulose is denoted by nano-structured cellulose which consist of C6H10O5. Since cellulose is abundant polymer in nature, large quantity of nanocellulose can be manufactured from the cost-effective aspect. Non-toxic and lightweight properties make it easy to carry, so it can be used in applications which requires mobility. High tensile, stiffness and electrical conductivity expand its usage through electrical and mechanical applications. Unique properties depending on the type of nanocellulose are also exist. There are three types which are cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), cellulose nanofibers (CNF), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC).
First type of nanocellulose is cellulose nanocrystal, development in applications show that CNCs have unique specialities for improving mechanical properties of nanocomposites such as electrospun nanocomposite fibers/mats and nanocomposite hydrogels. Numerous nanocomposite hydrogels reinforced with CNCs can be designed to be sensitive in fast temperature, pH, and salt for controlling drug delivery. In addition, specific applications such as energy-related materials, sensors, photonics, and barrier films can be developed by using CNC-reinforced nanocomposites fibers. For example, Park N. created electroluminescent nanocellulose paper at 2017, and one can adjust the color by changing the frequency of the electrical current.
Figure 1: Transmission electron microscopy images of the nanocrystalline cellulose: original magnifications 3150,000 (a) and 3100,000 (b).
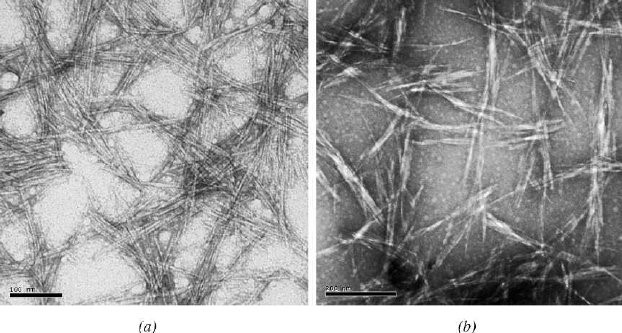
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/278724020_Nanocrystalline_Cellulose_Morphological_Physical_and_Mechanical_Properties
Second type of nanocellulose is cellulose nanofibers which are consist of long and thin fibers at nanometer scale which form a network, and, it has not only crystalline but also amorphous regions. In water, cellulose nanofibers exhibits viscosity characteristics. Furthermore, It shares some of the properties with cellulose nanocrystal such as light, tensile, stiffness, and barrier films, and it also has applications in foods, medicine, cosmetics, and health care. As an example for application, Nippon Paper Group commercialized effective antibacterial and deodorant sheets using CNF with TEMPO catalytic oxidation method.
Figure 2: FE-SEM cellulose nanofiber
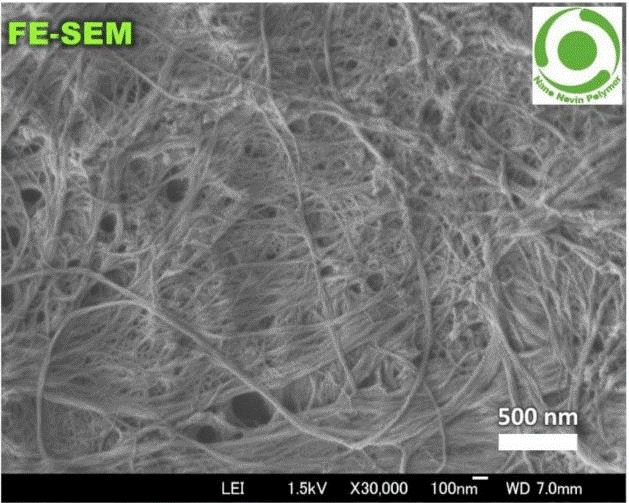

https://www.researchgate.net/publication/308073434_Improving_the_Properties_of_Soda_Bagasse_Pulp_by_Using_Cellulose_Nanofibers_in_the_Presence_of_Cationic_Polyacrylamide/figures?lo=1&utm_source=google&utm_medium=organi
Last type of nanocellulose is bacterial nanocellulose (BNC), and for various applications, numerous types of BNCs have been developed, such applications are tissue regeneration, drug delivery systems, vascular grafts, textile industry, nonwoven cloth, waste treatment, pharmaceuticals, and scaffolds for tissue engineering. Moreover, BNCs can improve mechanical properties of biomaterials. An example for applications is that BNC-based nanopaper can be used for tight ultrafiltration which is demonstrated by Mautner at 2015.
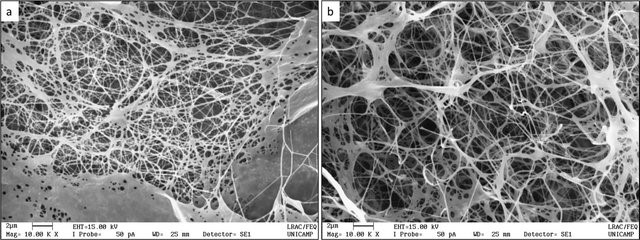
Figure 3: Scanning electron microscopy of bacterial nanocellulose membranes (a) and bromelain-loaded membranes (b).
Assoc. Prof. Sinan Keten who develops nanocomposites with nanocellulose, and supported by the Army Research Office and National Institute of Standards and Technology at USA. He said `Cellulose nanocrystals are an attractive alternative because they are naturally bioavailable, renewable, nontoxic, and relatively inexpensive, and they can be easily extracted from wood pulp byproducts from the paper industry.” He is working on bullet-proof glass created by nanocellulose, and he is honored with Presidential Early Career Award by President Obama.
Cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), cellulose nanofibers (CNF), and bacterial nanocellulose (BNC) are the three types of nanocellulose. In addition, the research directions mainly in photonics, medicine, biotechnology, electronic devices, surface functionalization, nanocomposites, foods, cosmetic, pharmaceutical, paper and paperboard, films and foams, and barriers.
Comments
Post a Comment