Doping means the introduction of impurities into a semiconductor crystal to modify the conductivity. The two important elements that silicon can be doped with are boron and phosphorus.
The dopant is integrated into the lattice structure of silicon and the number of outer electrons define the type of doping. Elements with 3 valence electrons are used for p-type doping, in this case is boron; 5-valued elements for n-doping, in this case is phosphorus. By doping boron or phosphorus the conductivity of silicon can be increased.
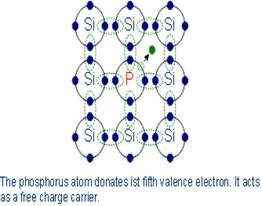
Phosphorus has an outer electron more than silicon. Four outer electrons combine with ever one silicon atom, while the fifth electron is free to move and serves as charge carrier.
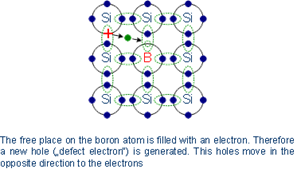
In contrast to the free electron due to doping with phosphorus, boron effect is exactly the opposite. Boron catches an additional outer electron, and leaves a hole in the valence band of silicon atoms. Therefore the electrons in the valence band become mobile.
Now let's see the applications of n and p doped silicon sputtering targets. We can obviously say that silicon sputtering targets have many advantages. By silicon sputtering we can eliminate toxic gas release. Also the temperature of sputtering process for silicon is lower. Another advantage of silicon sputtering target is that we can control the amount of H2 incorporated in the deposited film.
When we look at the applications of silicon thin film we can see that in semiconductor electronics doped silicon films have a great importance. There are many methods to obtain doped silicon films like plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition, hotwire chemical vapor deposition and magnetron sputtering. For these methods we can say that magnetron sputtering is an attractive technique in silicon thin film deposition. By magnetron sputtering of doped silicon you may obtain silicon thin film with higher carrier concentration and lower activation energy when we compare with undoped silicon.
If you need n or p doped silicon sputtering targets you may contact with us by clicking the links given below:
Comments
Post a Comment