What is Indium Oxide?
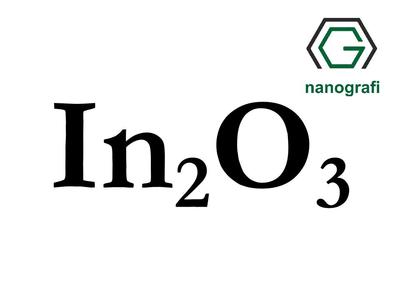
Indium Oxide is a chemical compound which consists of Indium metal and Oxygen. Indium Oxide is a yellow powder at room temperature. The melting temperature of Indium Oxide is 1910 oC which is very high.
Indium Oxide Nanoparticles/Nanopowder and Their Application Areas
Indium oxide nanoparticles/nanopowder have applications in electronics. Indium Oxide nanoparticles/nanopowder are applied in flat panel displays, transparent conductive electrodes, detectors and lasers. In gas sensors for Ozone and Nitrogen Oxide Indium Oxide nanoparticles/nanopowder are used. Indium Oxide nanoparticles/nanopowder are used as substitute for mercury as a battery inhibitor. Indium Oxide nanoparticles/nanopowder are also applied for optical and antistatic coatings. Indium Oxide nanoparticles/nanopowder form a transparent conducting ceramic in combination with Tin Oxide.
Technical Properties of Our In2O3 (Indium Oxide) Nanoparticles/Nanopowder, 18-68 nm, High Purity 99.996% Product
| Purity % | 99.996 |
| Color | light yellow |
| AVERAGE PARTICLE SIZE (nm): | 18-68 |
| Morphology | faceted and rods |
| SPECIFIC SURFACE AREA (m2/g): | >25 |
| Bulk Density (g/cm3) | 1,2 |
| True Density (g/cm3) | 7,2 |
| Manufacturing Method | chemical precipitation |
You may buy In2O3 (Indium Oxide) Nanoparticles/Nanopowder, 18-68 nm, High Purity 99.996% from the link given below:
Comments
Post a Comment