Carbon atoms bounded together to form repeated hexagon patterns is called Graphene, and it is considered as 2-d crystal structure. Due to its shape, it has unique properties such as both the strongest, and the lightest material in the world, most conductive, and transparent. Although the graphene is expensive and relatively hard to manufacture, effective and inexpensive graphene derivatives can be produced. Graphene oxide (GO) is one of these, and it is oxidized form of graphene, so one can make graphene via dispersion of graphene oxide in water and also other solvents. Graphene oxide is not a good conductor even it is considered as electrical insulator, but functionalization can be done depending on the application such as optoelectronics, bio-devices, and drug-delivery systems.
Figure 1: Graphene oxide
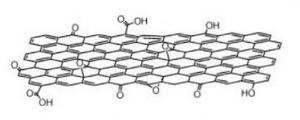
Since graphene oxide has oxygen functionalities, it can easily disperse in organic solvents also. Combining GO with polymers and ceramic matrixes is major benefit to boost mechanical and electrical properties. S.K. HAZRA and S.BASU concluded in their research at 2016 that graphene-oxide nanocomposites have promising applications on chemical sensing in terms of toxicity, inflammability, and explosive nature of chemicals.
Figure 2: Sensing mechanism for kaolin-GO nanocomposite
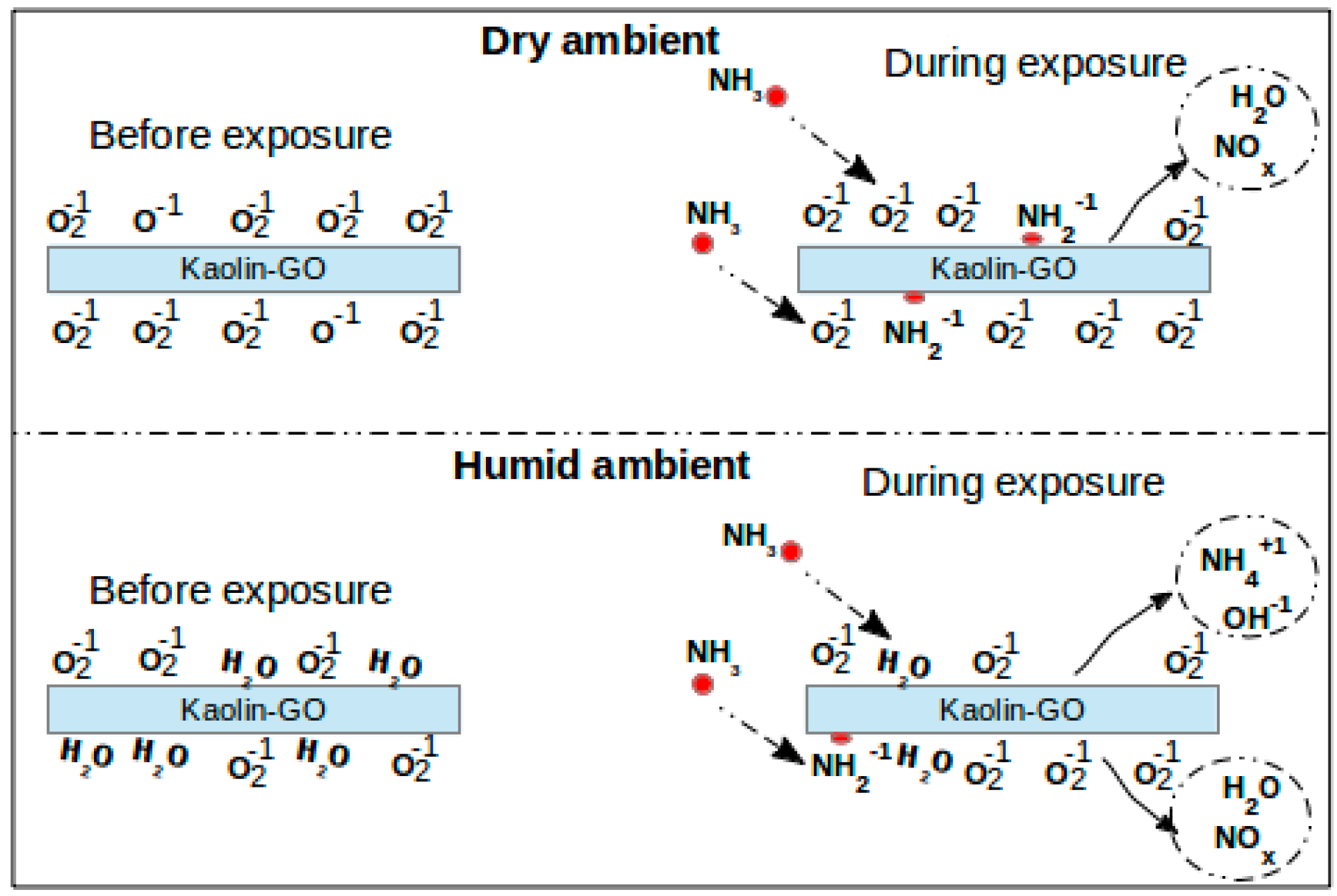
S.K. HAZRA and S.BASU, Graphene-Oxide Nano Composites for Chemical Sensor Applications, 2016
Not only in powder form but also in the form of films, graphene oxide have applications. First of all it can be dispersed easily to any substrate, so GO qualified for production of transparent films which are used for applications such as flexible electronics, solar cells, chemical sensors. As an example, conductive graphene nanowires can be written using graphene oxide as a electrically insulating layer. With atomic force microscope tip, oxygen in graphene oxide is removed when heat is applied. Therefore, one can write conductive circuits in the insulating graphene film.
Since graphene oxide has high surface area, it is capable of using in electrode material for batteries, capacitors and solar cells. For instance, according to Graphena, application of light GO layer with spray-coatad on a standard fiberglass seperator slowed the lithium ions moving through the battery to prevent formation of dendrites. Spread of dendrites through the electrolyte can lead the two electrodes to meet, so this situation causes explosion of battery.
Figure 3: Left: Dendrites forming on a lithium electrode. Right: Lithium plates uniformly on a lithium electrode in a battery with a graphene oxide nanosheet separator.
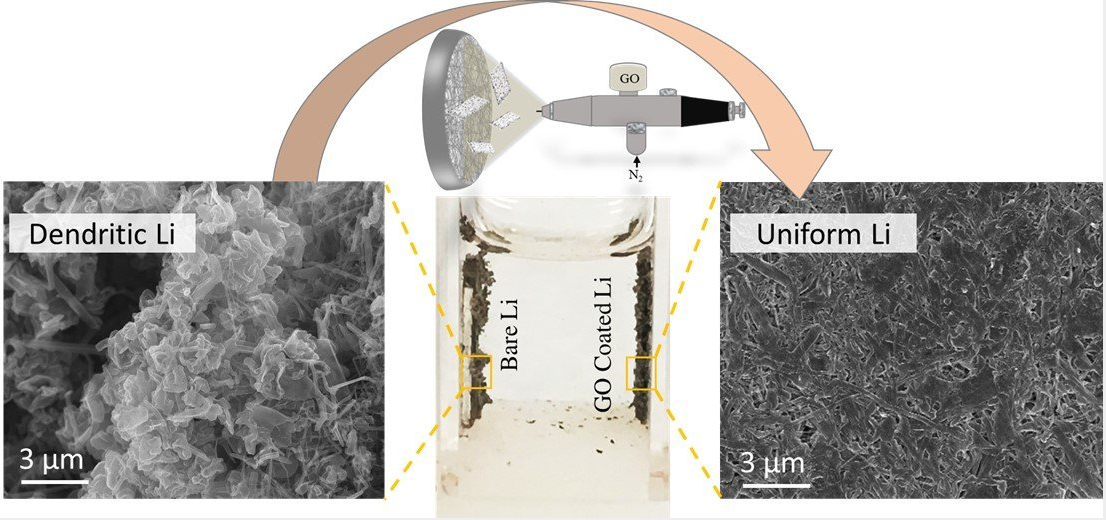
https://phys.org/news/2018-03-graphene-oxide-nanosheets-lithium-metal-batteries.html#jCp
Although graphene oxide is derivative of graphene, there are many fields that it is used. High surface area, and ability to be used in nanocomposites and as the film form with its properties make it a unique material for both research and industry. More applications will be found and the production methods will be developed in the near future.
Although graphene oxide is derivative of graphene, there are many fields that it is used. High surface area, and ability to be used in nanocomposites and as the film form with its properties make it a unique material for both research and industry. More applications will be found and the production methods will be developed in the near future.
Comments
Post a Comment