The nanopowder of Carbon Black is conductive and non-polluting. The applications of Carbon Black Nanopowder are versatile, the sectors involved are plastics, electronics, inks, coatings, and green technology. Carbon Black is predominantly used as reinforcing filler and in the rubber industry. Approximately, thirty grades of it are produced for this purpose so they impart a wide spectrum of properties to rubber products.
History of Carbon Black Nanopowder
Carbon Black is produced by different activities such as the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, including diesel and fuel oil, as well as the burning of firewood, among others. Carbon black was initially produced in China by incomplete combustion in oil lamps and intended to provide the black pigment of the Indian ink. In 1912, it showed exceptional qualities for rubber tire reinforcement.
Production Capacity of Carbon Black Nanopowder
In 2017, the global production capacity was 16 million t/year, 43% in China with about 100 factories. The productions of the European Union in 2017 was 1,890 million t. In 2017, Carbon Black's production was decreased in France to 50,000 t / year by stopping the operations at the Ambes plant. China's exports of black carbon in 2017 were 37% to Thailand, 20% to Indonesia, 11% to Vietnam, 10% to Japan, 8% to Taiwan.
Characteristics of Carbon Black Nanoparticles
The carbon black nanopowder consists of carbon (98 to 99.7%), present in the form of spherical particles (from 10 to 500 nm). Their specific surface is between 10 and 300 m2/g. There are many grades of carbon black, depending on the raw materials used, combustion conditions and thermal decomposition.
Industrial manufacturing of Carbon Black Nanoparticles
Carbon Black is produced mainly by incomplete combustion of heavy oil residues using the Oil Furnace Black process (used for 98% of world production). The reaction takes place in an oven in which natural gas is burned in the presence of excess air. The oil charge is introduced radically. The temperature ranges from 1400 to 2000 ° C and the reaction time from 1/100 to 1/10 of a second depends on the type of blackness desired. The combustion gases, containing the carbon black, are rapidly cooled by water spraying and the carbon black is recovered by filtration. For example, Orionused 4000 fiberglass handle filters, 3 m long and 15 to 20 cm in diameter. An inverted gas stream empties the filters alternately every 2 to 3 minutes. The purchase of the heavy oil charge represents more than 30% of the selling price. The production units have an average capacity of 75 t / day and, per plant, there are usually 2 to 5 units. The yields are about 50% of the carbon content of the feed.
In addition, the cracking of acetylene, with temperatures of over 2000 °C gives the purest carbon blacks and have a more conductive character.
Sources for the emission of Carbon Black
- Incomplete combustion of firewood, charcoal, and manure, used for the purpose of cooking.
- Combustion of diesel engines in vehicles.
- Burning of agricultural waste and forests.
- Extraction of fossil fuels.
- Burning garbage outdoors or "open sky".
6 uses of Carbon Black Nanoparticles:
- A 7 kg tire contains 3 kg of carbon black which gives it resistance to wear. An automobile (including tires) contains about 18 kg of carbon black. The treads use carbon black of about 30 nm (10 to 20 nm for fast and off-road vehicles. Fine blacks bring hardness; larger blacks retain the flexibility of rubber. Carbon black is currently used in the manufacture of green tires, partly competing with precipitated silica.
- Liquid inks for large prints (newspapers) contain nearly 10% of their mass of carbon black. Fat inks for the offset from 20 to 30%.
- Automotive paints, lacquers for furniture and pianos contain very fine carbon black nanopowder (10 to 20 nm).
- Carbon black (mass contents of 1 to 3%) provides the protection of plastics and elastomers against UV.
- Conductive carbon blacks (150,000 t / yr worldwide), obtained, in part, from acetylene, are used in saline electric batteries (40,000 t / year), high voltage underground cables (60,000 t / year), plastics and conductive rubbers...In the conductive cables, the black conductors are incorporated in the coating of the aluminum strands and thus ensure the equalization of the electric field and the prevention of the corona effect.
- It is also used as a model for diesel emission particles without sticking to metals and hydrocarbon.
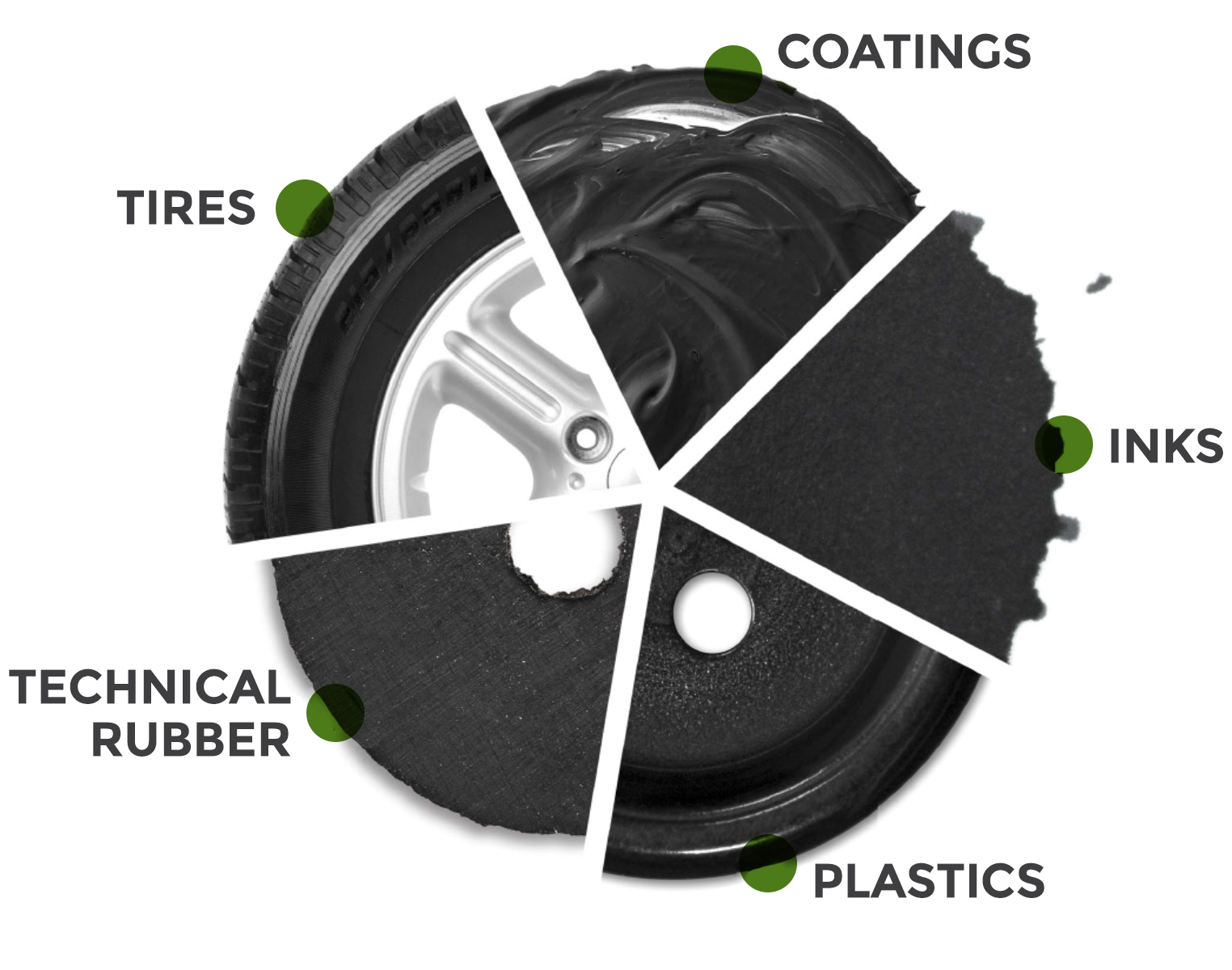
Image retrieved from: https://blackbearcarbon.com/products/
Use of Carbon Black Nanopowder in the Rubber Industry
As indicated above, the majority of the use of Carbon Black is in the Rubber Industry, it’s around 93%. This use can be characterized into 2 major groups: mechanical rubber goods and tires. The durability and performance of the rubber products are increased due to reinforcing characteristics of carbon black nanopowder. The use of Carbon Black in the rubber industry is classified as N100-N900 black series.
Use of Carbon Black Nanopowder in other sectors (Plastics, Coatings, Inks, etc.)
The rest 7% use of carbon black nanopowder is in different sectors, which includes coating, inks, and plastics. More applications involve toners, batteries, sealants, etc. In these products, the blackness, UV light protection, and conductivity properties of carbon black nanopowder are used.
Additionally, the below sectors also benefits from reinforcing, staining, and UV protection properties of Carbon Black nanopowder:
- Aerospace industry
- Boat coatings
- Home appliances
- Computer cases
- Furniture
- electronics
- General industry
- Pipe coatings
- Nava industry
- Rubber for non-automotive applications
- Films for packaging
In summary, Carbon Black nanopowder is an important element that has various significant uses in various sectors. The majority of its use is found in the rubber industry and the minor use is found in some other sectors, as indicated above. The product has great potential for future applications.




Comments
Post a Comment